China and the United States are intensifying competition in space technology, with both countries planning to build data storage and processing facilities in outer space in the coming years.
China has announced plans to establish space-based data centers within the next five years, aiming to process and store data directly in space rather than relying on Earth-based infrastructure.
This ambitious goal mirrors similar plans by SpaceX, the American aerospace company founded by Elon Musk, which is also exploring the possibility of building data storage facilities in space within the next two to three years.
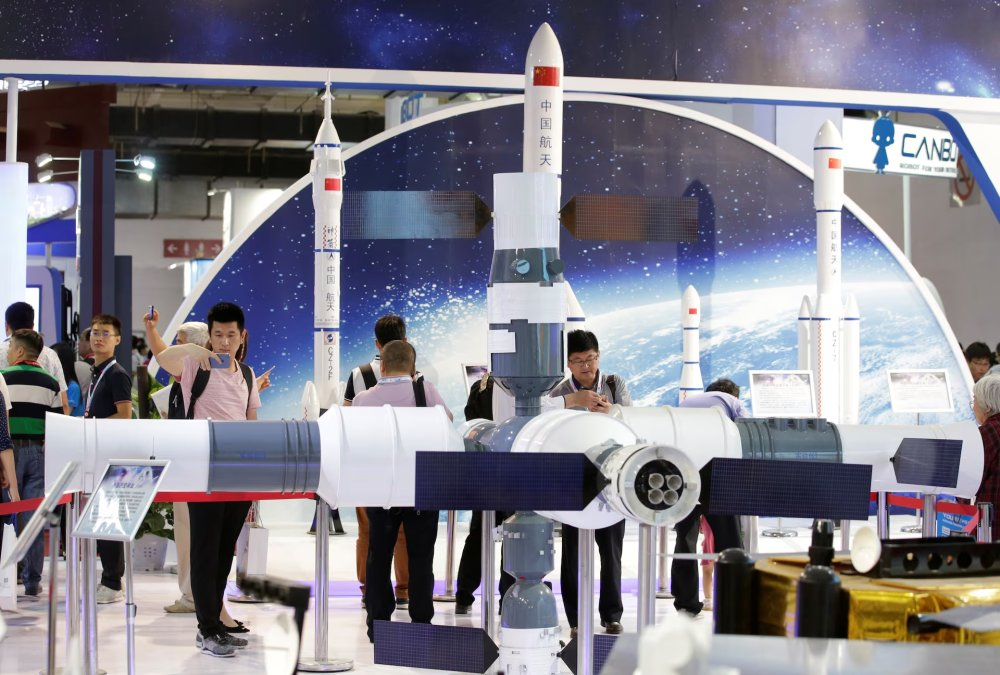
China’s Space Data Center Plans
China’s state-owned aerospace company, China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), is leading the project. The company plans to develop space technology powered by solar energy, allowing data centers in orbit to operate independently of Earth-based power systems.
According to Chinese officials, the technology is expected to be fully operational by 2030. Once completed, it will be capable of receiving, processing, storing, and transmitting massive volumes of data, marking a major shift in how digital infrastructure is managed.
By processing data in space, China aims to reduce pressure on terrestrial energy systems and improve efficiency in handling large-scale information.
Elon Musk and SpaceX’s Vision
Elon Musk has also expressed interest in deploying space-based data centers, arguing that storing and processing data in space could help address energy shortages on Earth.
Musk believes that space data infrastructure could eventually become more cost-effective, especially as renewable energy sources such as solar power are more abundant and uninterrupted in space.
Although SpaceX has not announced a fixed timeline, Musk indicated that the project could be realized within two to three years, depending on technological readiness.
Growing Space Rivalry Between China and the US
The race to build data centers in space reflects a broader geopolitical and technological rivalry between China and the United States. Both nations view space as a critical domain for economic growth, technological dominance, and military strength.
China has stated its ambition to become the world’s leading space power by 2045. However, experts note that several challenges remain, including the development of reusable spacecraft and long-term sustainability of space infrastructure.
China Expands Space Exploration and Tourism
Beyond data storage, China is actively investing in advanced space research technologies and has announced plans to expand activities related to space exploration and tourism.
These initiatives signal China’s long-term strategy to establish a strong and diversified presence in space, positioning it as a major competitor to established space powers.
The Future of Data Infrastructure
As global data consumption continues to rise, space-based data centers could reshape the future of digital infrastructure. However, experts caution that technical, financial, and regulatory challenges must still be addressed before such systems become widely operational.
For now, the competition between China and the United States highlights how space is increasingly becoming the next frontier in the global technology race.