Rwanda is making significant progress in the peaceful use of nuclear technology, particularly in healthcare, energy, and medical research, as part of its long-term development strategy.
On November 28, 2025, the Council of Ministers approved cooperation agreements that will allow nuclear medicine services to officially begin in Rwanda.
These advanced medical services are expected to become operational in 2026.
What Is Nuclear Medicine?
Nuclear medicine is a specialized branch of medical imaging that uses small, safe amounts of radioactive substances to diagnose and treat diseases.
It falls under advanced diagnostic imaging, a field that remains limited in many countries due to the high cost of equipment and technology.
Key Machines to Be Used
Nuclear medicine mainly relies on two advanced imaging systems:
- Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT)
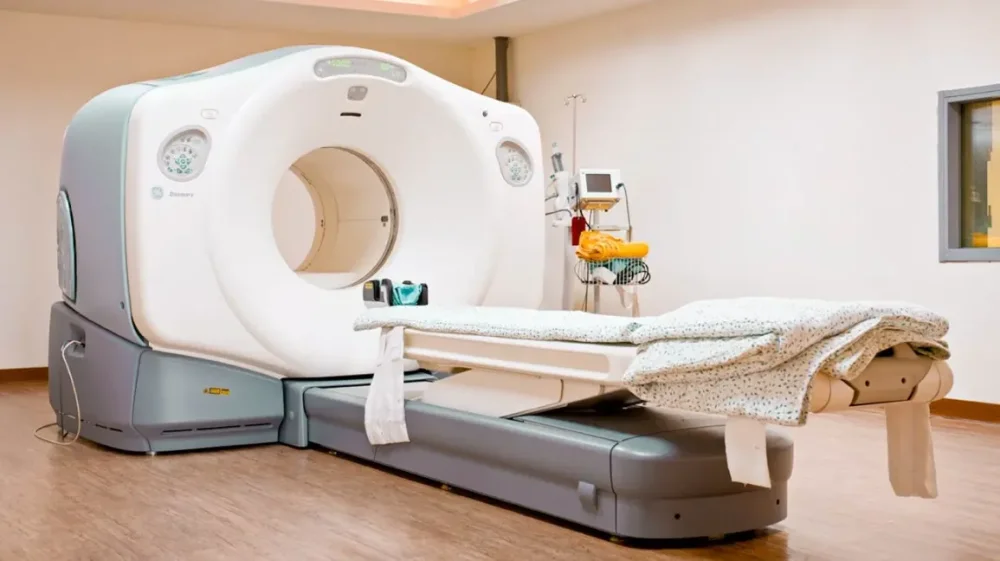
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET Scan)
Rwanda has opted to acquire PET Scan technology, which is more advanced and precise.
How PET Scan Works
Patients receive a small injection of radiotracers, substances derived from nuclear technology.
These tracers travel to areas affected by disease.
A special scanner then detects their movement and produces detailed images showing biological activity inside the body, not just physical structures.
This method helps detect diseases that do not appear on conventional scans.
Diseases Diagnosed Using Nuclear Medicine
PET Scan is especially effective in diagnosing and monitoring:
- Cancer
- Heart diseases
- Brain and neurological disorders
- Vascular conditions
It allows doctors to locate disease at an early stage and plan treatment with high precision.
Improved Accuracy in Cancer Treatment
Nuclear medicine enables surgeons and oncologists to see exactly where a tumor is located.
This reduces the risk of unnecessary surgery and damage to healthy tissues.
It is particularly important for brain cancers, where even minor errors can have severe consequences.
International Partnership Behind the Project
The nuclear medicine program is being implemented through a partnership between the Government of Rwanda and Aegle Onco Care Center Ltd, a specialized healthcare provider based in Mauritius.
Services to Be Offered at Military Hospital Kanombe
The services will be based at Rwanda Military Hospital in Kanombe, Kigali.
This hospital also hosts the Rwanda Cancer Centre (RCC), making it a strategic location for advanced cancer diagnosis and treatment.
PET Scan Equipment Already Procured
In May 2025, the Minister of Health, Dr. Sabin Nsanzimana, told Parliament that Rwanda had completed all requirements to acquire PET Scan equipment.
He confirmed that the machines were expected to arrive before the end of 2025.
Cyclotron Technology to Support Services
The nuclear medicine unit will also use a Cyclotron, a machine that produces radiotracers used during PET Scan procedures.
Most of the required equipment has already been secured.
This technology allows detection of early-stage cancers at the cellular level.
Strengthening Rwanda’s Cancer Care Capacity
The new services will complement existing cancer treatment options in Rwanda.
These include MRI, CT Scan, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and surgical oncology.
Future Expansion to King Faisal Hospital
Once renovations at King Faisal Hospital are completed, increasing capacity from 167 beds to 600 rooms, the facility is expected to install two PET Scan machines.
Dr. Augustin Sendegeya, Medical Director at King Faisal Hospital, confirmed that nuclear imaging is included in the hospital’s expansion plan.
Reducing Medical Referrals Abroad
The introduction of nuclear medicine will significantly reduce the number of patients referred overseas.
Rwanda will gain the ability to diagnose diseases at a cellular level, detect illnesses early, and treat them more effectively.
This milestone strengthens Rwanda’s position as a regional hub for advanced cancer care.